This year, the field group of the GPS Laboratory (LGPS) based on the Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) method conducts planned field measurements of GNSS network points on the territory of the Chui, Jalal-Abad, Talas, Issyk-Kul, Naryn regions of Kyrgyzstan within the framework of the State Assignment: "Study of modern movements of the earth's crust of the Tien Shan and adjacent territories by methods of ground and space geodesy" reg. No. 1021052806451-5-1.5.1.
Repeated surveys of the same GNSS points in the study area make it possible to determine the high-precision position of the point at the time of measurement and track the long-term rate of its displacement to solve fundamental geodynamic problems, as well as to assess the danger to the population and vital facilities. From May to September 2024, LGPS employees traditionally carry out two campaigns (KGS24a from 04.07.2024 to 03.08.2024; KGS24b from 21.08.2024 to 16.09.2024).
Each team includes an operator and a driver of a ZIL-131 or GAZ-33088 vehicle. Each team measures 14-15 points per month, with 36 hours allocated for each point. The vehicle mileage during one campaign was 1,500-2,200 km. The average vehicle mileage between observation points was 130 km. Since 2020, GSDN employees have been taking GNSS measurements using Russian-made MP-8 receivers capable of recording signals from 4 satellite constellations: GPS, GLONASS, Beidou and SBAS (Fig. 2).
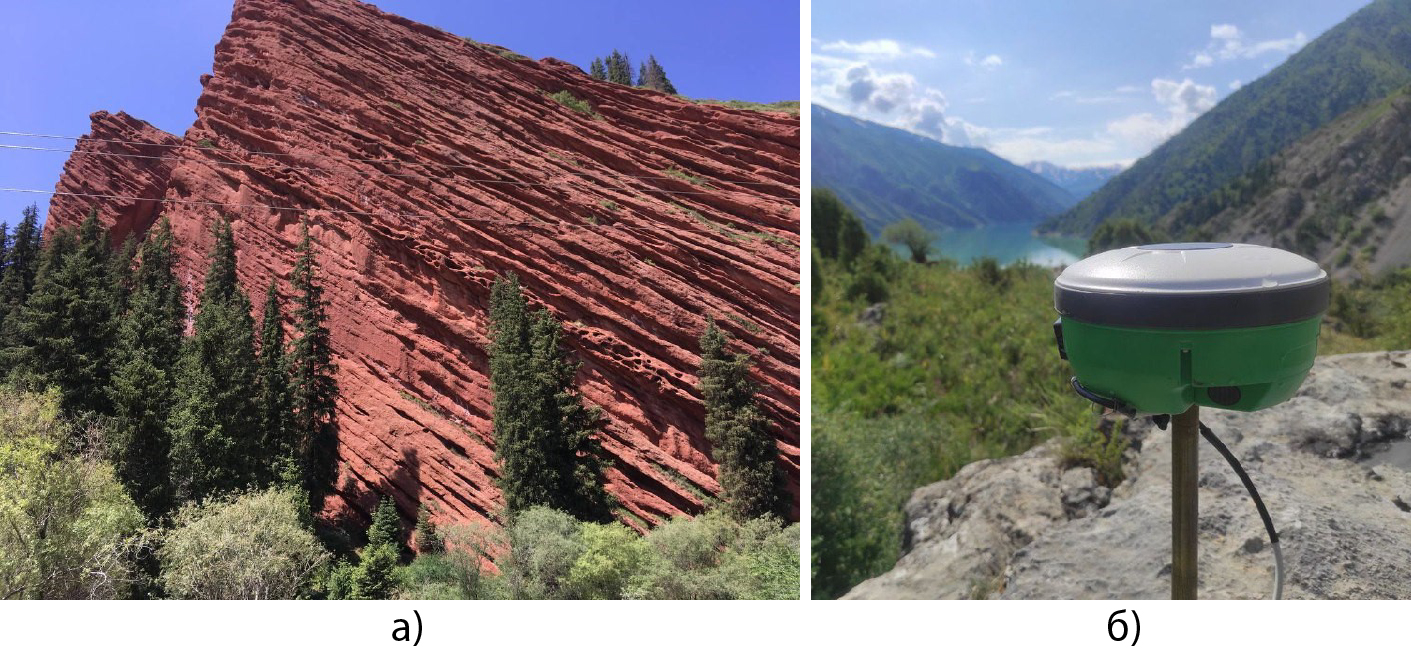

Figure 1 – Fragments of field GNSS work in 2024:
a) Field landscape of the team from the measurement site of the regional GNSS point;
b) Measurement at the GNSS point with the MP-8 receiver with a pin support.