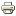
This year, employees of GPS laboratory (RS RAS) conducted routine field measurements of the Kyrgyz GPS network sites based on the Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) method. Annual repeated surveys of the same GPS sites on the study area allow to fix the high-precision position of the site at the measurement time and to track the multi-year rate of its displacement to solve fundamental geodynamic problems, as well as to assess the danger of the population and vital objects.
From May to September 2021, two campaigns (KGS21a from 25.05.2021 to 25.06.2021; KGS21b from 17.08.2021 to 15.09.2021) were carried out for measure regional sites on the territory of Kyrgyzstan (Fig.1).
Till 2020 the employees of the GPS Laboratory conducted measurements mainly with the Topcon Legacy-E instruments, which allow fixing the signals of GPS and GLONASS satellite systems. In the current year the works are carried out with the use of new generation devices of Russian production MR-8, which in addition to the 2 main ones are able to record additional information from the Beidou (China) and SBAS (Satellite Based Augmentation System) systems. These devices are much lighter and more compact, have an integrated design of the receiver with the antenna (Fig.2).
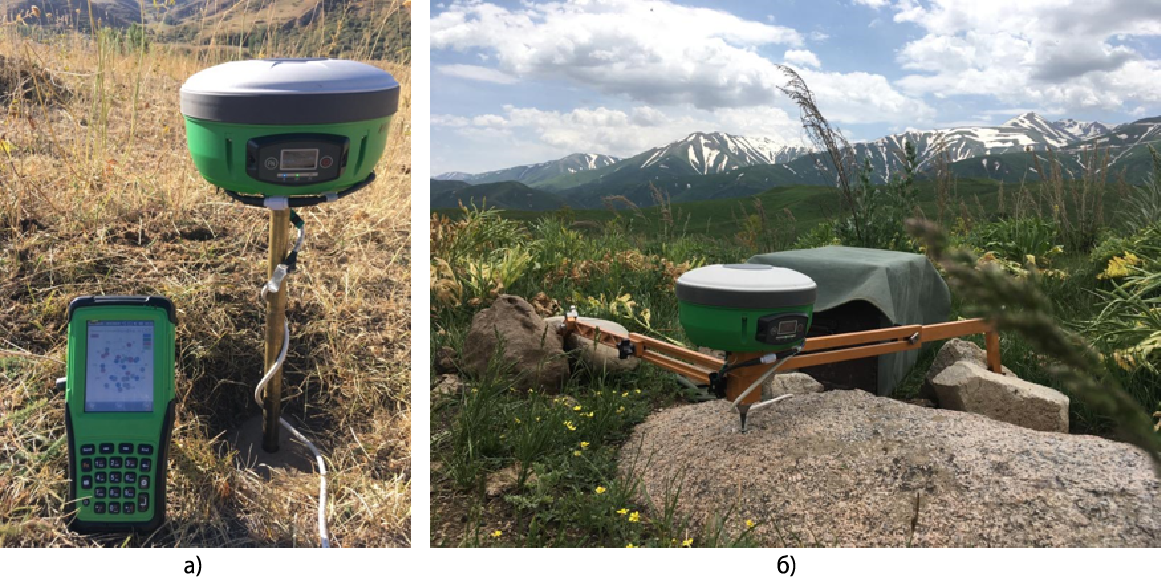

Figure 2 - GNSS receiver MR-8 under field regional measurements 2021:
Last Updated on Friday, 24 September 2021 15:30